Before a fixed asset is created in Microsoft Dynamics NAV, the system should be pre-configured with the right setup depending on any given company needs. For more information about these setups, refer to Fixed Assets Series 1-3 in these series of tutorials.
1. Go to Department. Under Financial Management, select Fixed Assets.
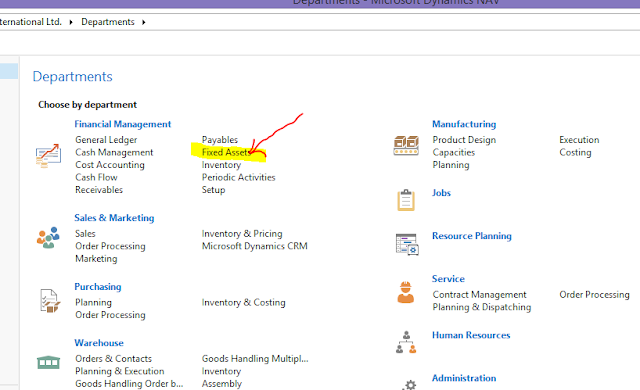 |
| Fig 2: Fixed Assets - Department |
2. On the next page select Fixed Assets.
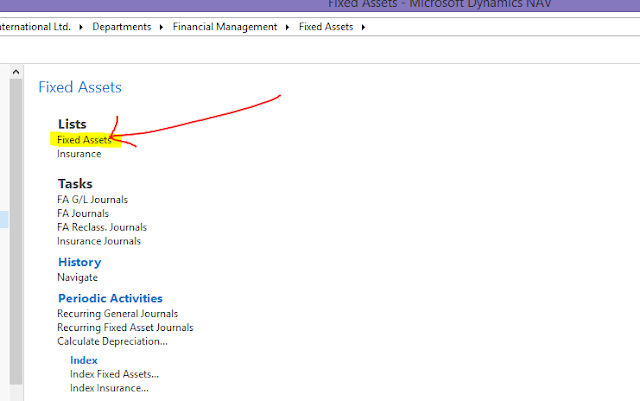 |
| Fig 3: Fixed Asset |
3. Click New or press the shortcut keyboard keys – CTRL + N.
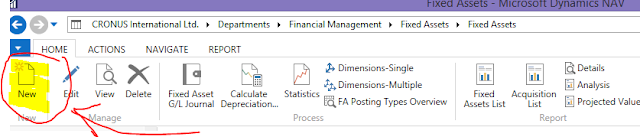 |
| Fig 4: Fixed Asset - New |
4. At this point a new window is opened. This is a fixed asset card. This card contains three fast tabs. These include General fast tab, Depreciation Books fast tab and Maintenance fast tab.
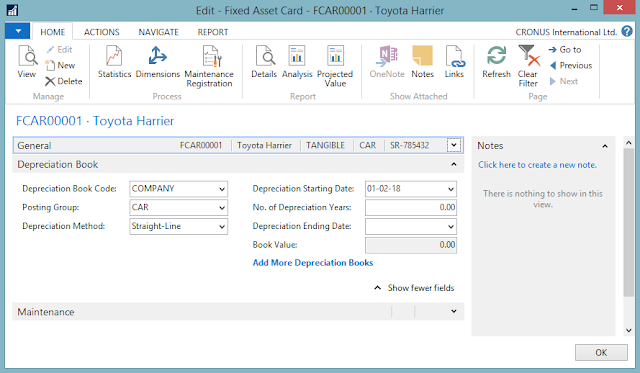 |
| Fig 5: Fixed Asset Card |
5. Under the General fast tab, fill in the following fields:
• No. (MANDATORY) such as FCAR00001. Click on AssignEdit button to assign a specific number series.
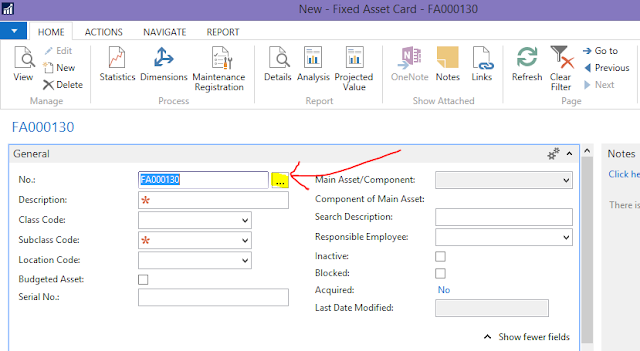 |
| Fig 6: Fixed Asset - AssignEdit |
Select the respective number series from the No. series list window and click OK.
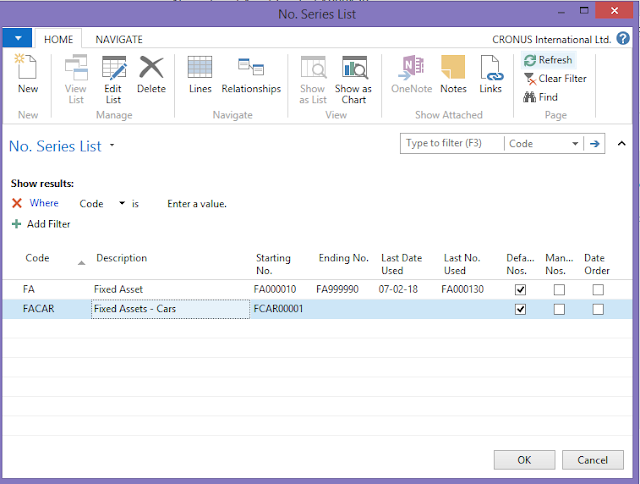 |
| Fig 7: Fixed Assets - No Series List |
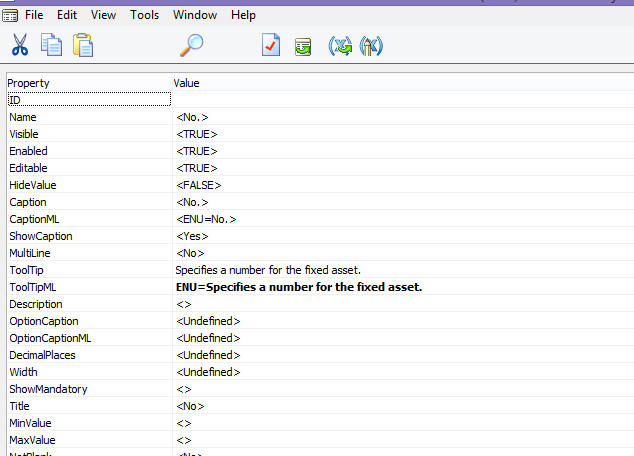
(This step should be carried out by the developer of the system) However, if you do not see this field, the developer of the system has got to add it from the development environment of the database. From the development environment Go to Page 5600 (Fixed Asset Card), design this page, select field No., go to its properties. You will find DocNoVisible on the Visible Property. Remove DocNoVisible from this property. Save the page 5600 - Fixed Asset Card object. At this point you should be able to view the No. field from the Fixed Asset Card.
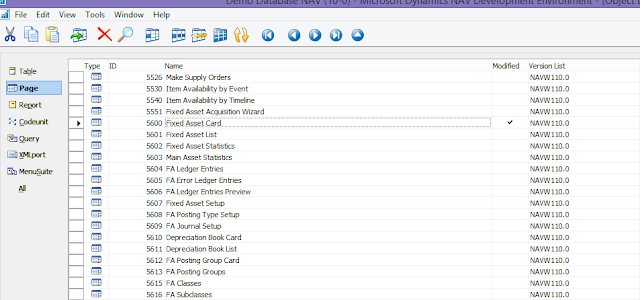 |
| Fig 8: Development Environment |
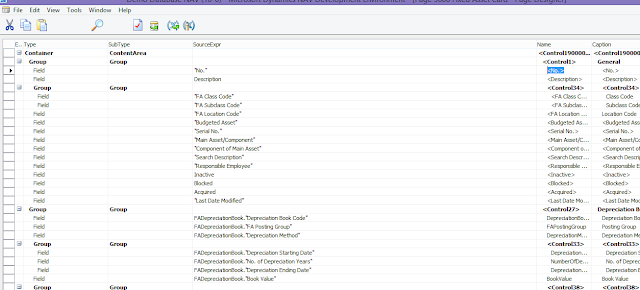 |
| Fig 9: Development Environment |
 |
| Fig 10: Development Environment |
• Description. This is the description of the fixed asset, such as Toyota Harrier.
• Class Code. Specifies the class the fixed asset belongs to such as CAR. This can be any group you decide to categorize your company assets. You may have motor vehicles, furniture and so on.
• Location Code. Specifies the location such as the building where a fixed asset is located.
• Budgeted Asset. Specifies if the asset is for budgeting purposes. If this is checked, then the asset is for budgeting purposes.
• Serial No. Specifies the fixed asset serial number.
• Main Asset / Component (UN-EDITABLE). Specifies if a fixed asset is a main asset or a component of a fixed asset.
• Component of fixed asset. Specifies the number of the fixed asset.
• Search Description. Specifies a search description for the fixed asset.
• Responsible Employee. Specifies which employee is responsible for the fixed asset.
• Inactive. Specifies that the fixed asset is inactive (for example, if the asset is not in service, or is obsolete).
• Blocked. Specifies that transactions with this fixed asset cannot be posted. Blocked fixed assets will be omitted in batch jobs that create journal lines for fixed assets posting. For example, if you run the calculate depreciation batch job, if an asset is blocked (field is checked), it will be omitted in the fixed asset journal lines created.
• Acquired (UN-EDITABLE). Specifies if the fixed asset was acquired. For example, if a purchase invoice of a fixed asset is posted, it creates an entry with Acquisition Cost FA Posting Type and it changes the Acquired field on the asset card to Yes.
• Last Date Modified (UN-EDITABLE). Specifies when the fixed asset was last modified.
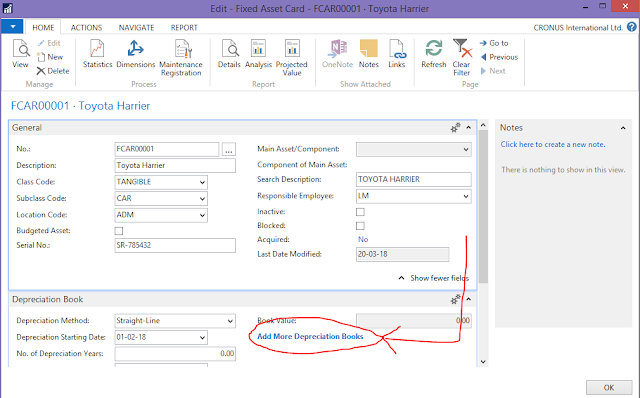
6. Under the Depreciation Book fast tab, fill in the following fields: (You can select – Add More Depreciation Books in order to view more fields)
• Depreciation Method. - Specifies how depreciation is calculated for the depreciation book.
• Depreciation Starting Date. – Specifies the date on which depreciation of the fixed assets start.
• No. of Depreciation Years. – Specifies the length of the depreciation period, expressed in years.
• Depreciation Ending Date. - Specifies the date on which depreciation of the fixed assets end.
• Book Value (UN-EDITABLE). - Specifies the book value of the fixed asset as a FlowField.
A FlowField can be thought of as a virtual field, which is an extension to the table data. For example, if you click the Book Value flowfield on the fixed asset card, it will open another window showing the table data - fixed asset ledger entries.
Assuming you are using straight line percentage or Straight-Line % instead of number of depreciation days, you will leave both the Depreciation Ending date and No. of depreciation fields empty.
 |
| Fig 11: Fixed Asset - Depreciation Book |
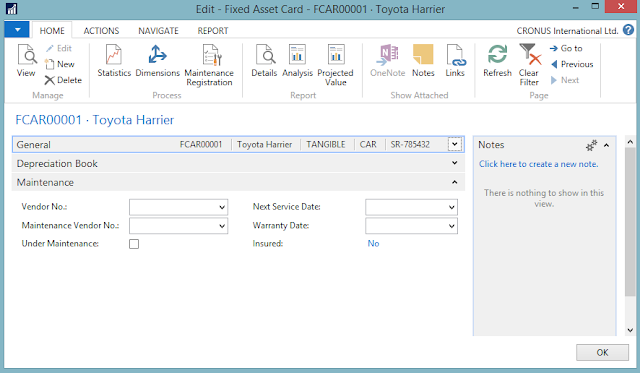
7. Under the Maintenance fast tab, fill in the following fields:
• Vendor No. - Specifies the number of vendor from which you purchased this fixed asset.
• Maintenance Vendor No. - Specifies the number of the vendor who performs repairs and
maintenance on the fixed asset.
• Under Maintenance. Specifies if the fixed asset is currently being repaired.
• Next Service Date. Specify the next scheduled service date of the fixed asset. This is used as a
filter in the Maintenance – Next Service report.
• Warrant Date. Specifies the warranty expiration date of the fixed asset.
• Insured (UN-EDITABLE). Specifies that the fixed asset is linked to an insurance policy.
 |
| Fig 12: Fixed Asset - Maintenance |
8.
Close the fixed asset. You have successfully created an asset in Microsoft Dynamics NAV. For more information about Microsoft Dynamics NAV, you can visit
www.adroitltd.com or
www.facebook.com/Adroit.ASL - Microsoft Dynamics NAV Uganda at Adroit Solutions Limited.
You can leave your comment or question in the comment section.














This idea is mind blowing. I think everyone should know such information like you have described on this post. Thank you for sharing this explanation.Your final conclusion was good. We are sowing seeds and need to be patiently wait till it blossoms.
ReplyDeleteAsset Management Software
Asset Tracking Software
Asset Management Software India
Asset Management Software Chennai
I’ll definitely digg it and personally recommend to my friends. I’m sure they’ll be benefited from this site..
ReplyDeleteAsset Management Software
Asset Management Software Abu Dhabi
Asset Tracking Software
IT Asset Management Software
Fixed Asset Management Software